The central processing unit, the processor, is arguably the most crucial component inside a computer. As the “brain” of the device, the CPU executes instructions and performs calculations that power everything we do with our computers, from gaming and video editing to web browsing and office tasks. So, to truly understand how computers work at their core, it’s crucial to understand what a CPU is and its role.
This guide will deeply dive into CPUs by exploring their history, components, functions, and types. We’ll examine how a CPU operates through its fetch-decode-execute cycle. We’ll also investigate essential CPU considerations like clock speed, cores, and heat management. By the end, you’ll comprehensively understand one of the most fundamental parts of any computing device. So let’s get started!
History and Evolution of CPUs
The earliest CPUs date back to the 1940s when vacuum tubes were used for circuitry. They were enormous, power-hungry machines that only governments and large institutions could afford. The 1950s saw the advent of smaller and more reliable transistors than vacuum tubes. This “transistor switch” revolution enabled mainframe computers to shrink considerably. In the 1960s, integrated circuits packed multiple transistors onto a single silicon chip, further reducing size and cost. By the 1970s, microprocessors placed the entire CPU onto an integrated chip, ushering in the era of personal computers. Moore’s Law has continued shrinking transistors ever smaller, exponentially increasing their number and CPU’s power.
Main Components of a CPU
Several key components work together to enable a CPU’s functions:
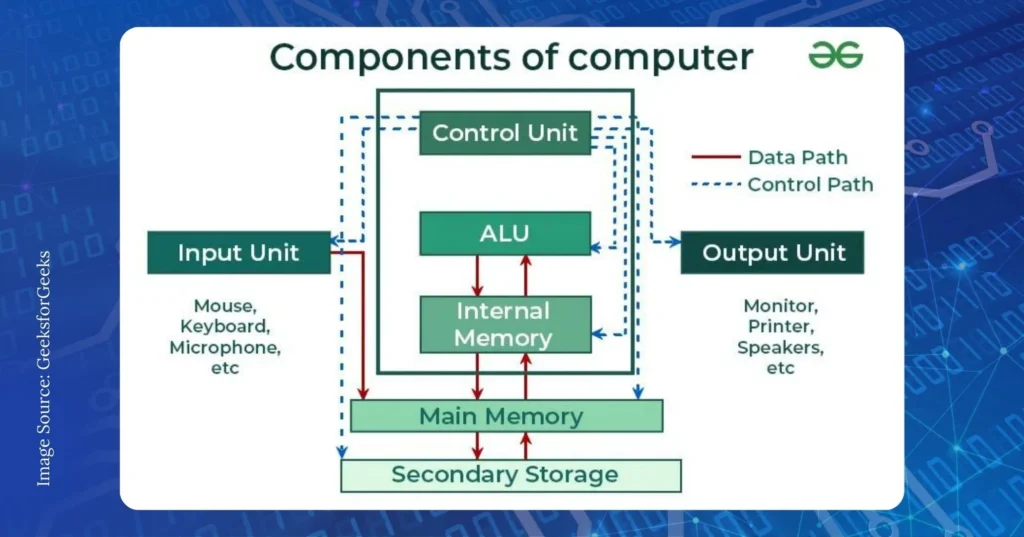
- Control Unit: The control unit orchestrates all activity inside the CPU by continuously monitoring instructions and issuing commands. It decodes instructions to determine the required operation and activates circuitry accordingly.
- Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU): The ALU performs basic math and logical operations like addition, subtraction, AND, and OR. The control unit routes inputs to the ALU, executing the specified operation.
- Registers: Registers are where data and instructions are temporarily stored during processing. Types include accumulators, general-purpose registers, and program/instruction registers. They provide high-speed access.
- Cache: The cache is high-speed memory within the CPU that stores copies of frequently used data/instructions to avoid slow central memory retrieval each time. This improves memory access time.
These core components smoothly transfer data, perform calculations, and manage instruction flow according to the CPU’s fetch-decode-execute cycle, enabling efficient processing.
Read also: Steps To Do When Your Intel CPU Keeps Crashing
How a CPU Works
A CPU carries out program instructions through a repeated process known as a fetch-decode-execute cycle. This fundamental sequence is how a CPU functions at its core. Let’s examine the critical stages of this cycle.
Fetch-Decode-Execute Cycle
At its core, a CPU continuously follows a fetch-decode-execute cycle to process instructions:
- Fetch – The control unit directs the program counter register to retrieve the following machine code instruction from memory.
- Decode – The instruction is analyzed to identify the specific operation required.
- Execute – The CPU performs the instruction, such as an arithmetic operation using the ALU or loading/storing data to/from memory.
This cycle repeats many billions of times per second as the CPU rapidly fetches and executes one instruction after another according to the program flow. It’s the fundamental repeated mechanism that powers all computation.
Arithmetic Operations
When an instruction requires numeric calculation, such as adding two values, the ALU springs into action. The control unit routes the operands from their locations (usually registers) into the ALU inputs.
It then performs the specified arithmetic operation – perhaps addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division. The result is then stored in a register or memory for subsequent use. Standard arithmetic instructions involve incrementing/decrementing values and performing binary logical shifts.
Logical Operations
The ALU also handles logical or bitwise instructions comparing or transforming data at the binary level. Examples include AND, OR, NOT, XOR, and comparisons for equality/inequality. These allow manipulation and testing of individual bits within registers and memory.
By altering specific bits, programmers can represent high-level computer science constructs like Boolean logic and set operations. Logical ops are heavily used for bitmasking, flow control, and bit-banged peripheral I/O like GPIO pins.
Control Operations
Beyond raw calculations, the CPU coordinates the overall system through control-oriented responsibilities. The control unit directs execution flow by conditionally branching code and changing the program counter. It also manages interrupts to prioritize events like I/O requests.
Other duties involve synchronizing multi-core processors, scheduling threads across cores, and supervising co-processors/accelerators. Control signals mediate information pathways between the CPU and system components like memory, storage, graphics cards, and peripherals.
Types of CPUs
As computing demands evolved, different CPU designs emerged to suit diverse needs. CPUs now come in several varieties optimized for particular workloads. Let’s explore the primary types of CPUs available.
Single-Core CPU
The original CPU designs of yesteryear only contained one processing core within a single package. Single-core CPUs can execute one instruction at a time in a sequential workflow.
They dominated computing for decades but became ill-suited to today’s parallel world, demanding multi-task performance. Single-core machines still meet essential workloads but aren’t suitable for extensive multitasking or demanding programs that benefit from parallelism.
Multi-Core CPU
As transistor counts ballooned in the 2000s, CPUs evolved to pack multiple independent cores in a single chip. Whereas each core has its own set of ALUs and execution resources, all share the same caches, memory interface, and I/O logic.
Multi-core designs allow distribution work across parallel threads to accelerate processing dramatically. Almost all modern general-purpose CPUs contain multiple cores, with high-end designs sporting dozens. Workloads ideally leveraging N cores will theoretically see a maximum Nx speedup over single-core performance.
Dual-Core, Quad-Core and Beyond
Early multi-core CPUs featured just two or four cores (dual-core and quad-core). However, core counts have steadily marched upwards, with today’s highest-end desktop CPUs boasting eight cores or more. Server CPUs often have over 16 cores; some specialized models extend beyond 32 or 64 cores for massively parallel applications.
More cores generally correlate with improved multitasking muscle at the cost of higher thermals, power use, and per-core performance. For most mainstream PCs, quad-core or six-core CPUs provide a nice balance of grunt and efficiency.
Specialized CPUs
In addition to general CPUs, processor architectures are tailored for specific niches. Graphics processing units (GPUs) have thousands of small cores that can handle the data parallelism of computer graphics efficiently.
Field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) allow the programming of custom circuits for unique workloads. Application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) are permanently hardwired for a sole function like crypto mining.
Digital signal processors (DSPs) handle real-time audio/video processing. Even smartphone system-on-chips (SoCs) integrate specialized graphics, cellular modems, and more into a CPU package. Specialized chips often outperform general CPUs for their intended domains.
Managing CPU Performance
A CPU’s true capabilities depend on properly leveraging its internals and specifications—factors like cores, clock speed, and cooling all impact performance. We’ll cover techniques for optimizing a CPU’s speed and handling loads.
Cores and Threads
Multi-core CPUs require software to split work across threads that distribute across cores, allowing tasks to leverage multiple cores for increased performance. Hyperthreading also boosts performance by faking extra threads.
Clock Speed
A CPU’s clock rate directly affects its processing speed. While higher clocks improve performance initially, they also drive up heat and power usage. Modern architectures instead emphasize optimizations like parallelism.
Heat Management
Excess heat degrades CPU components, so cooling takes priority through heatsinks, fans, liquid cooling, and case ventilation. Throttling occurs when CPUs reduce clocks under thermal duress. Dust cleaning also helps temperatures.
Overclocking
Power users can exceed factory CPU speeds through overclocking but with decreased reliability. It requires voltage, clock increases, and proper cooling to handle extra thermal loads. Stability depends on silicon quality and cooling method. Tools help maximize stable performance gains.
Read also: Intel Z890: Thunderbolt 4 & Arrow Lake CPU with 4 Xe Cores
Choosing the Right CPU
- Performance requirements – Consider tasks like gaming, content creation, office work
- Budget – CPU costs range from $50-1000+
- Compatibility – Match CPU socket to motherboard
- Thermal design power – Ensure cooling supports the TDP workload
- Future upgradability – Consider upgrade paths when initially buying
Conclusion
In conclusion, the CPU defines a system’s capabilities as the core computational component. Grasping its internal anatomy, fetch-decode-execute workflow cycle, and optimization factors provides valuable insight into fundamental computing principles.
Cores, threads, clocks, and thermal specifications influence performance depending on workloads. Choosing the right CPU requires balancing a system’s intended uses, budget, and future upgrade potential. CPU innovation also remains pivotal for enabling progress in software, technology, and beyond.



















