Intel instructs Motherboard Manufacturers to set “Default Settings” as the BIOS standard by May 31 to fix stability problems with 14th & 13th Gen.
The tech community has had ongoing discussions regarding the stability issues with Intel’s 13th and 14th-generation processors. Reports of crashes were prominent from many users while running CPU-intensive applications and games. Some notable examples are Adobe Premiere Pro, Tekken 8, Hogwarts Legacy, and other Unreal Engine titles.
In response to the volume of complaints, Intel addressed the OEM motherboard manufacturers with a specific request regarding the default BIOS settings on their platforms. Let’s deep dive into this issue and see how events have unfolded.
The Stability Problem
An alarming number of reports surfaced detailing crashes encountered across various use cases. Intensive video editing in Premiere Pro and AAA gaming titles were prime examples where the systems would suddenly lock up or reboot unexpectedly.
After investigating the problems, it was discovered that motherboard vendors had aggressively adjusted the power profiles to maximize advertised performance benchmarks. While leading to gains on spec sheets, these customizations fell outside of Intel’s specifications and proved unstable for many average consumers.
The crashes highlighted that the current configuration was not viable and required addressing at the hardware level through updated BIOS settings.
Intel’s Request to Motherboard Makers
In reaction to the increasing number of unhappy customers, Intel formally communicated with its OEM partners and system builders. They were asked to ensure end-users receive motherboards with a default BIOS setting aligned to Intel’s recommendations. This “Intel Default Settings” profile would serve as the new standardized baseline rather than the varied customized profiles previously used.

All stock system builders were requested to implement this profile as the default option by May 31st, 2024. Intel viewed the default profile changes as key to resolving the stability issues many users experienced in their day-to-day activities and workloads.
What are the Power Profiles?
The power profiles define the allowable power limits and current thresholds for Intel’s latest CPU designs. Baseline, Performance, and Extreme are the three predefined levels. The conservative Baseline caps PL1 at 125W and PL2 at 188W, while Performance raises PL2 to 253W.
| Profile | PL1 (Watts) | PL2 (Watts) | PL4 (Watts) | Iccmax (Amps) | Iccmax. app (Amps) |
| Baseline | 125W | 188W | 293W | 249A | 200A |
| Performance | 125W | 253W | 380W | 307A | 245A |
| Extreme | 253W | 253W | 380W | 400A | 320A |
The more aggressive Extreme maxes out both PL1 and PL2 at 253W. Most vendors had shipped using the Extreme preset. However, this provided inadequate stability margins for many average users. The new Intel Default Settings mandate returns motherboards to the more modest Baseline configuration by limiting PL2 to 188W.
Performance Trade-Offs
Reducing PL2 power limits from 253W to 188W means performance enthusiasts can expect benchmark scores and intensive workload speeds to experience a tangible decline. CPUs can no longer pull extra watts for those brief turbo boost spikes.
This will negatively impact multicore rendering times and benchmark results published in early reviews. Avid gamers and creators may need to manually tune profiles to eke out every last frame or shave precious seconds off renders. How a lower long-term power draw will age Intel’s cutting-edge process nodes remains unseen.
Motherboard Makers Comply With Deadline
Major motherboard makers like ASRock, Biostar, ASUS, and MSI have acknowledged Intel’s request. BIOS updates are rolling out across platforms like Z790 and Z690 to comply with the May 31st deadline. These will set the conservative Baseline profile as the new default.
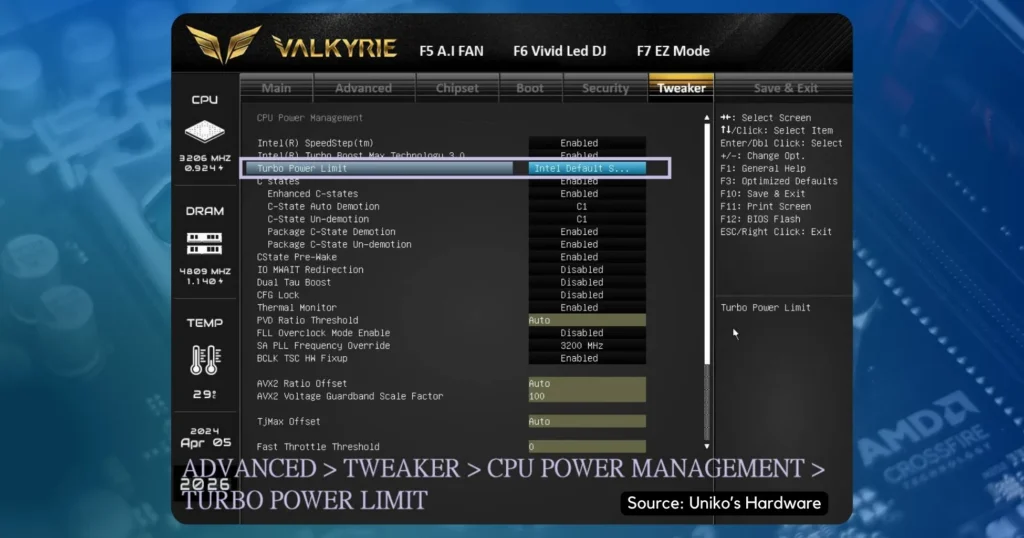
Intel Default Setting in BIOSTAR Z790 Valkyrie BIOS
While displeasing power users, the long-term hope is improved stability for the majority. Only future compatibility testing will reveal if the underlying issues were indeed addressed.
In Conclusion
In setting standard power limits, Intel aimed to curb widespread crashing issues plaguing its latest CPUs. While lowering default performance, stability for most users should increase once motherboard vendors complete the BIOS rollouts.
Enthusiasts still wanting more power have options to tweak profiles. However, the entire saga highlighted Intel’s lack of planning and communication, which contributed to the problem in the first place. Only time will tell if things are indeed fixed.



















